Table of Contents
Documentation
| Topic | Link |
|---|---|
| Getting Started | Getting Started |
| Using the Simulator | Using the Simulator |
| Using Vehicles | Using Vehicles |
| Using Walkers | Using Walkers |
| Sensors | Sensors |
| Data collection | Data collection |
| Creating own maps | Creating own maps |
| Building from source on Linux | Building on Linux |
| Building from source on Windows | Building on Windows |
| Installing on Linux | Installing on Linux |
| Installing on Windows | Installing on Windows |
Prerequisites
In this section, you will find essential information regarding the system requirements, software installations, and other dependencies necessary before starting the development of AGRARSENSE.
The project directory structure is as follows:
System Recommendation
- 9th gen Intel i5/i7/i9 or newer / 2nd gen AMD Ryzen 5/7/9 or newer
- 16+ GB RAM or more
- NVIDIA RTX-2000 series or newer.
- AMD RX-6000 series or newer.
- Intel Arc A-Series Graphics Cards or newer.
- 150+ GB disk space for source version
- 10+ GB disk space for packaged version
- Ubuntu 20.04 / Ubuntu 22.04
Quick Guide
- Install pre-compiled Unreal Engine 5.6 for Linux or follow Unreal Engine section to install AGRARSENSE fork of the Engine (preferred). Note if you use Unreal Engine 5.6 from Epic games launcher Instance segmentation camera doesn't work, as well some of our other engine related optimizations are not present.
- Clone AGRARSENSE repository
- Compile and open the project:
- Optional: Install ROS, follow ROS related installations section
Unreal related installations
Unreal Engine
You can either install pre-compiled Unreal Engine 5.6 for Linux by following this guide, or you can install our fork of the Unreal Engine which is preferred.
We have made our own fork of the Unreal Engine where we have made few optimizations to the engine to improve sensors performance.
To install our fork of the engine, you need to have a GitHub account linked to Unreal Engine's account.
Note. Compiling Unreal Engine from source will take ~1-4 hours depending on your CPU!
To build our fork of the Unreal Engine:
1. Clone the repository
2. Navigate to cloned folder:
3. Run the configuration scripts and compile the engine:
If you are installing the Unreal Engine for the first time on your machine, these commands will to prompt register Unreal Engine types and ask for sudo password. Click yes and enter sudo password to be able to compile the engine.
If you modify the Unreal Engine source after first compilation, you must compile the Unreal Engine again with following command. Unreal Engine will only compile the parts you have modified, not the entire Unreal Engine.
Set Unreal Engine environment variable
In order to AGRARSENSE to find the correct installation of Unreal Engine, we need to set the environment variable.
To set the variable for this session only:
To set the variable so it persists across sessions:
1. Open ~/.bashrc or ./profile.
2. Add the following line to the bottom of the file:
3. Save the file and reset the terminal.
Clone & Build AGRARSENSE
1. Clone the repository
2. Navigate to AGRARSENSE Unreal project folder
3. Build AGRARSENSE
To compile and open the Unreal Editor with one command
ROS related installations
ROS1 and ROS2
ROS noetic is required for the project to be able to communicate between Unreal Engine and ROS. The simulator supports ROS2 via ROS1 to ROS2 bridge.
ROS noetic is only offically supported on Ubuntu 18.04 and 20.04. Ubuntu 22.04 doesn't offically support ROS noetic.
AGRARSENSE Unreal project will work without a ROS installation but you cannot get or send any data to or from the simulator.
Install ROS noetic:
Install ROSBridge
https://github.com/code-iai/ROSIntegration states this: The recommended way to install rosbridge is from source (requires the rosauth package) – Even though you could install rosbridge using apt, there have been numersous issues where these apt packages do not reflect the code in the ros1 branch. Hence, it is best to install from source.
Install from apt packages:
When launching ROS server, you can launch it manually from Ubuntu Terminal:
To run python scripts with ROS connection you need to install Python ROS packages:
If connection doesn't go through from windows to Ubuntu WSL, you need to set **"ROS_IP"** in command prompt.
When ROS is installed follow this guide to install ROS2 (Foxy).
First, you need to install ROS2 without ros1_bridge.
First Launch new terminal and do following:
After ROS2 is build from source (without ros1_bridge), You need to 'source' both ROS1 and ROS2.
then build only ros1_bridge
NOTE: To use ROS1 rosbridge_server, you shouldn't add both ROS1 and ROS2 to ~.bashrc, since it mixes the packages. Instead, use ROS1 as intended and source ROS2 ONLY when needed
By typing ROS2 in terminal, it sources the ROS2 bash file and removes ROS2 alias
Using & testing AGRARSENSE
To test everything works correctly you can the following:
- Open new terminal and Launch Unreal Editor
- Start ROS1 with new terminal
- Start ROS1 to ROS2 Bridge with new terminal
- In Unreal Editor navigate to Content/Agrarsense/Maps/TestMaps/SensorShowCase and open SensorShowCaseMap level
- Press play
- Spawn wanted sensors through the user interface
- Open new terminal and type following command to see all current ROS topics
Visualizing sensor output with rviz
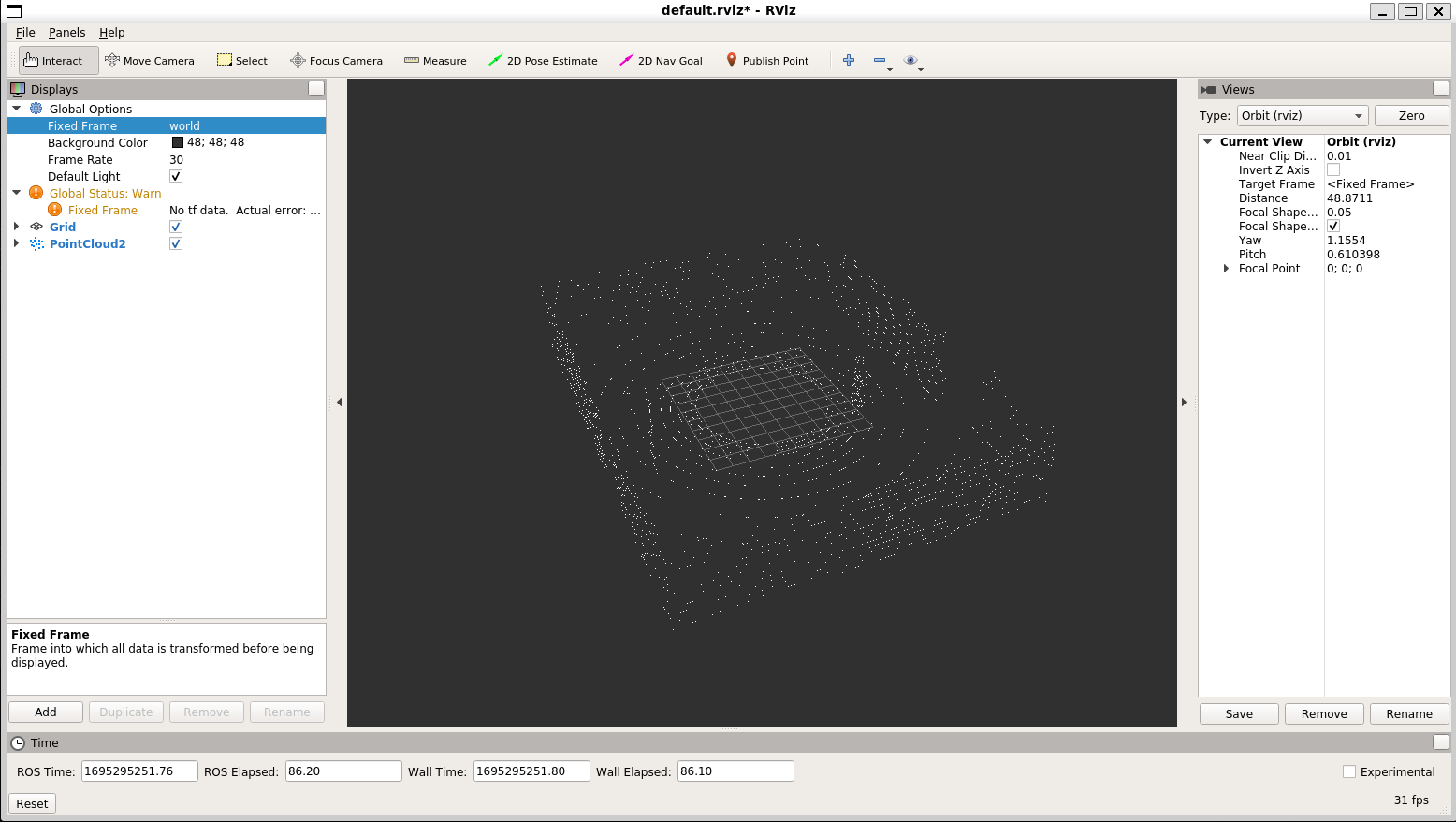
rviz is short for ROS Visualization. It's easy way visualize ROS messages, for example camera images and Lidar pointclouds.
- First follow Testing AGRARSENSE
- Open new terminal and launch rviz
- Now that rviz is open click 'Add' from the bottom left corner. This opens new window. In the window click 'By topic' tab. This tab should show all topics that rviz is able to visualize. For example if you have Lidar sensor active in the simulation, you should see /Agrarsense/Sensors/Lidar0/PointCloud2. Select that and click ok.
- Click 'Fixed Frame' and rename it to world and you should now see Lidar sensor pointcloud being visualized.
Creating packaged build
To create packaged shipping build for disturbution, you can either:
A. Create package without opening the Unreal Editor with following command. This script packages the project into ./Build folder
B. or launch the Unreal Editor with following command and create the package in the Unreal Editor.
Maps to include in the packaged build is defined in DefaultGame.ini file.
Modifying AGRARSENSE source
When modifying Blueprints or Widget Blueprints in Unreal Editor, simply click compile and save in the Unreal Editor as in with any Unreal project.
When modifying AGRARSENSE Unreal project C++ source or plugins C++ source, you must close the Unreal Editor, compile C++ and then open the Unreal Editor again or else changes will not take effect. This can be done with same scripts as above.
Note. Unreal Engine does support compiling C++ in Unreal Editor through Live Coding but your experience may vary.
To compile and open the Unreal Editor with one command:
To just compile C++ source and plugins: